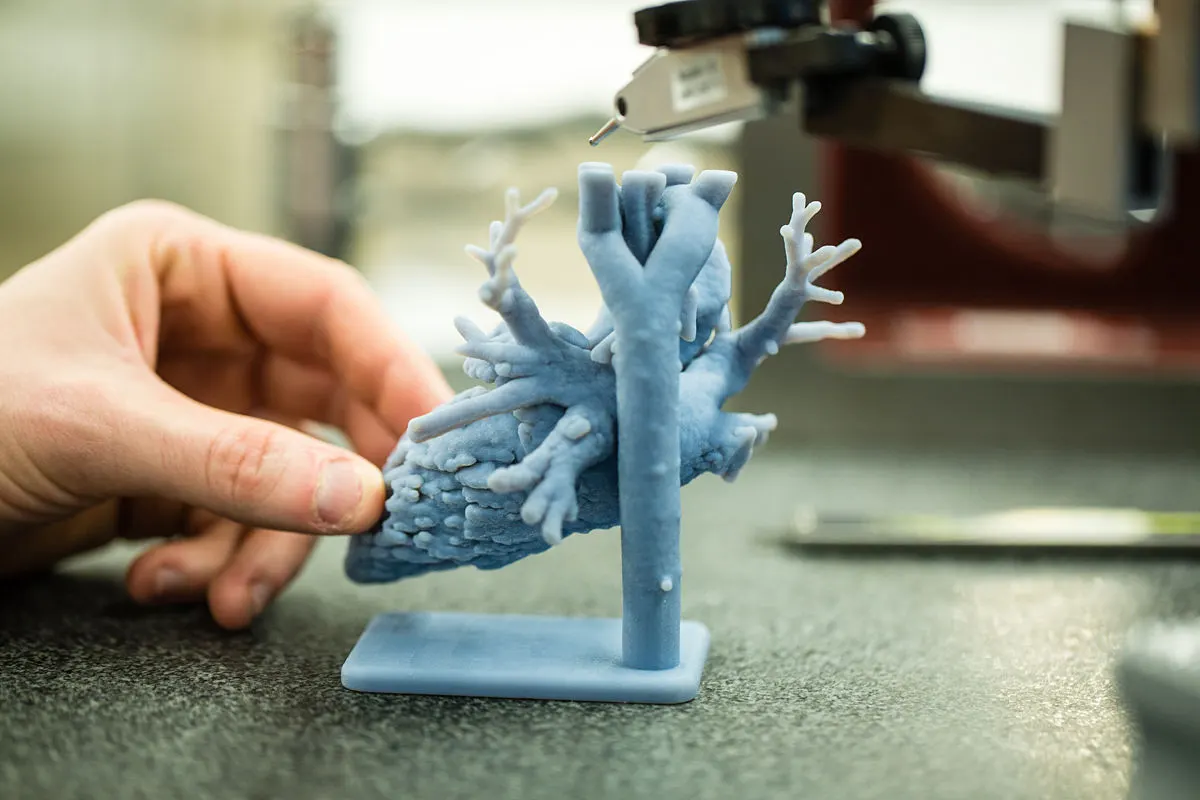
It’s no secret that innovation comes with a price. As technology advances, we’re often left wondering how these developments will affect our wallets. One such innovation is Digital Light Processing (DLP) 3D Printing. This revolutionary technology has transformed numerous industries, from healthcare to manufacturing. But how much does it really cost to operate a DLP 3D printer?
In this article, we’ll unravel the true cost of DLP 3D Printing. We’ll explore the initial investments, recurring expenses, consumable costs, and even the hidden expenditures you might not consider. Given the vast application and life-changing benefits of this technology, it’s essential to understand the financial implications before diving in headfirst.
This comprehensive guide aims to arm you with the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions about DLP 3D Printing.
The Fundamentals of DLP 3D Printing
DLP or Digital Light Processing is one term that’s grown increasingly prevalent in various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare.But what is it really about?This article plans to take you on an enlightening journey into the world of DLP 3D Printing.
What is Digital Light Processing (DLP)?
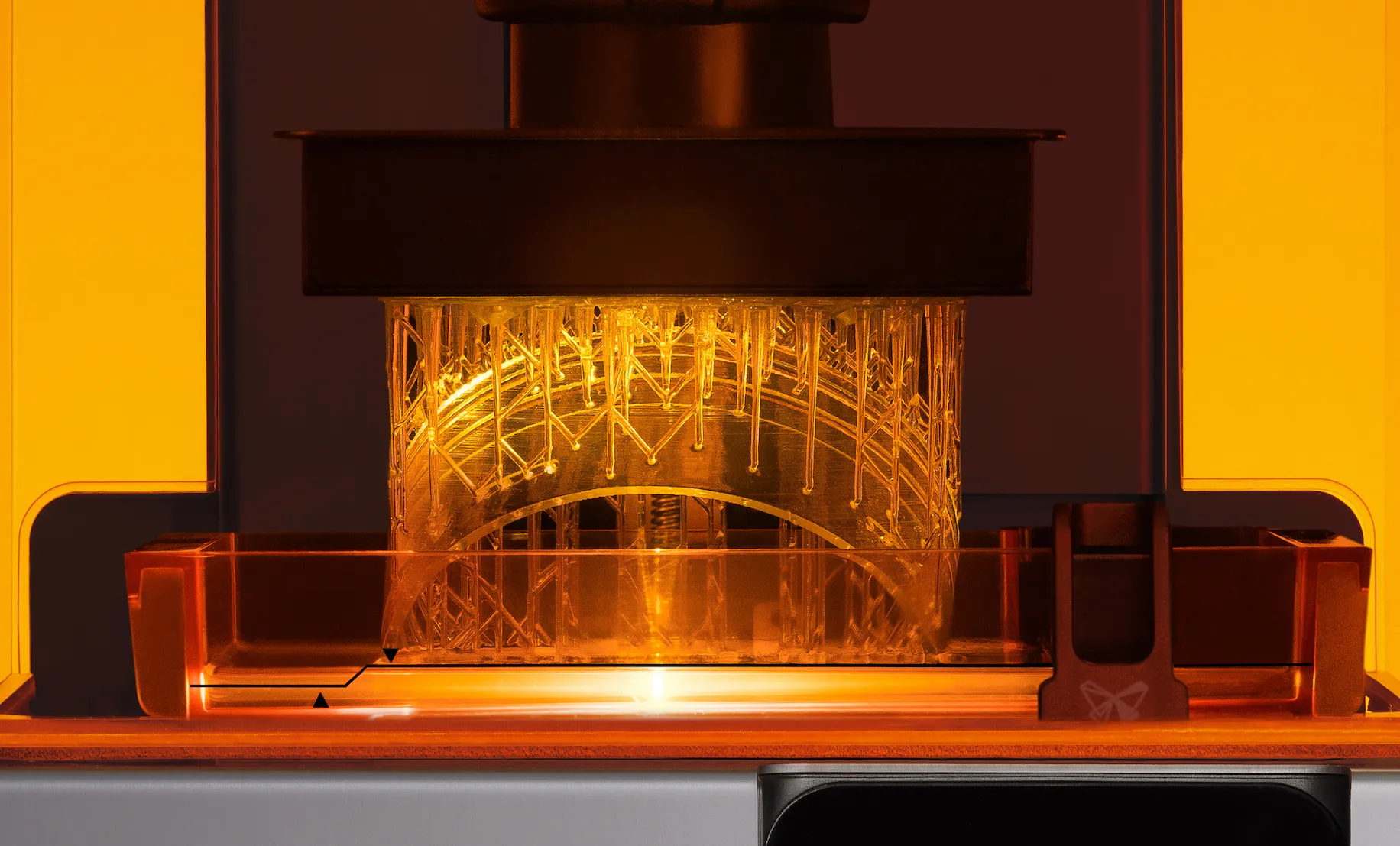
The term DLP stands for Digital Light Processing, a form of 3D printing that utilizes light and photosensitive polymers to create high-resolution prints. It was invented in 1987 by Larry Hornbeck of Texas Instruments.
Here’s the gist: a DLP printer creates 3D printed objects through a process known as photopolymerization, which involves hardening a liquid resin with light. This light-source is typically an ultraviolet light, and it shines on the resin, solidifying it layer by layer until the object is complete.
How Does DLP 3D Printing Work?
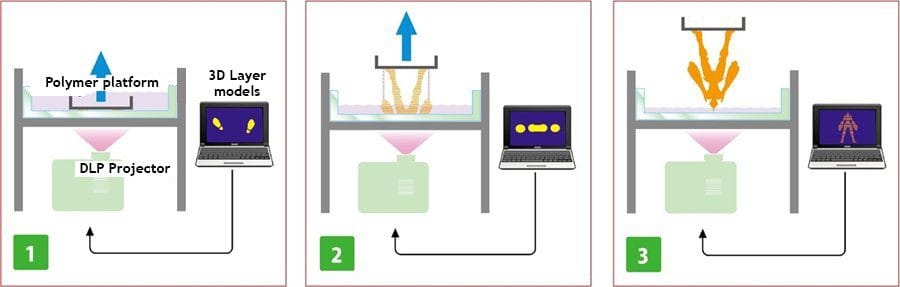
Let’s break down the process:
- Resin Bath: A build platform is submerged into a vat of photoreactive resin.
- Exposure to Light: An ultraviolet light source then projects images of each layer onto the surface of the liquid resin bath.
- Layer Formation: The light causes the resin to solidify, forming a single layer of the 3D object.
- Repetition: The platform then rises, and the process is repeated for each layer until the 3D object is complete.
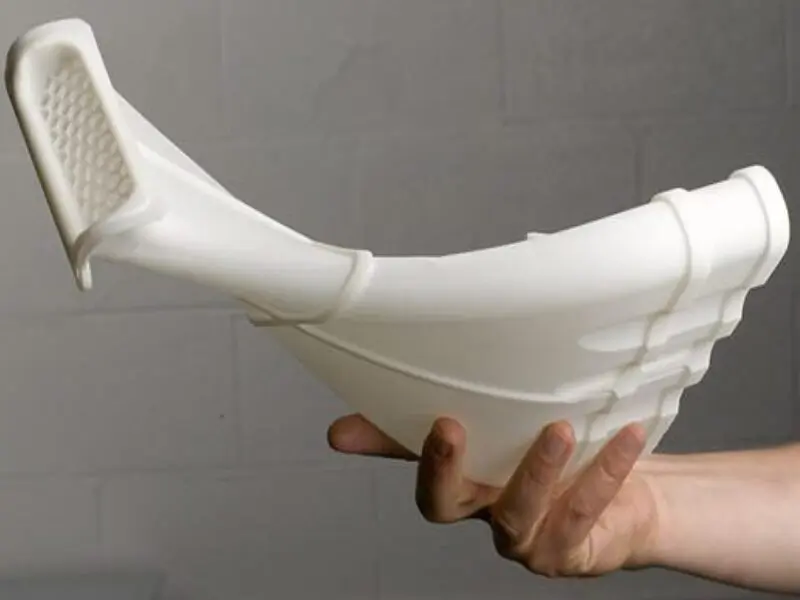


Components of a DLP Printer
Understanding a DLP printer’s components can help you grasp its working better. Here are the main elements:
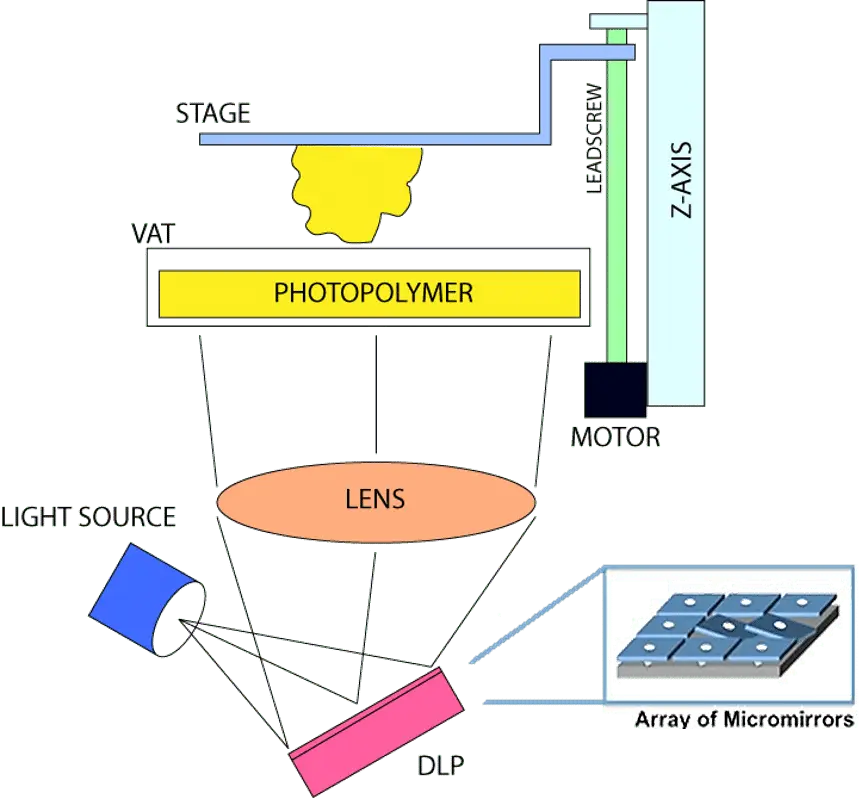
- ResinVat: Holds the liquid resin for printing.
- Build Platform: Where the object is built, layer by layer.
- UV Light Source: Used to cure and harden the resin.
- DLP Chip: Handles the projection of images for each layer onto the resin surface.
To conclude, DLP 3D printing is a fascinating field with vast potential. Understanding the basics of the technology can serve as a stepping stone to uncover how its applications could revolutionize several industries in the modern world.
Understanding the Costs of DLP 3D Printing
Every technological leap comes with its own set of costs, and DLP 3D printing is no exception. So, whether you’re a hobbyist or a business, it’s crucial to know what these expenses entail. Brace yourselves as we dive deep into understanding the real costs of operating a DLP 3D printer.
Initial Investment: Purchasing a DLP Printer
The first and arguably the most significant cost is the upfront investment of acquiring the DLP 3D printer. The price varies greatly, from hundreds to tens of thousands of dollars, primarily dependant on:
- The resolution: High-resolution printers tend to be more expensive
- The size of the printer: Larger printers that can produce bigger prints are priced higher
- The manufacturer: Established brands might demand a higher price for their tried and tested machines.
Ongoing Costs: Maintenance and Repairs
Like any piece of technology, maintenance will incur costs. For DLP 3D printers, this could include:
- Periodic Maintenance: Cleaning the vat, replacing the build platform etc.
- Repairs: While most DLP printers are built to last, they may occasionally need repairs. Be it a broken part, or a technical fault, be prepared for incidental repair charges.
Consumable Costs: Resin, Trays, and Other Supplies
DLP 3D printing cannot function without its heart – the resin. There are numerous types of resins, each with its own price point. On average, a liter of resin can cost anywhere between $50 to $200 based on its properties.
Additionally, certain components of printers, such as resin vats or trays, are considered consumable parts. Over time, these trays require replacement, adding to your operational costs.
By understanding these various factors that contribute to the cost of DLP 3D printing, you can make an informed decision about whether this technology is the right fit for you.
The Hidden Costs of DLP 3D Printing
Beyond upfront, ongoing, and consumable costs, DLP 3D printing carries a cost that often isn’t factored in – the hidden costs. These are expenses that don’t manifest themselves upfront but accumulate over time.
Power Consumption
Though not burning a hole in your pocket, the electrical costs associated with running a DLP printer should be noted. Energy consumption varies per printer model. However, a DLP printer generally doesn’t consume a lot of power. Be sure to check the power rating of your specific machine for a more precise estimation.
Training Costs
Operating a DLP printer often requires technical knowledge and skills. Therefore, training costs can be a substantial hidden cost. Whether it’s an online course or hiring a trainer, you’ll need to factor this in.
Waste Material
It’s inevitable – with 3D printing comes waste. Failed prints or excess support structure often result in wasted resin, which can pile up the cost over time. Another item to note is the disposal of this waste. Proper disposal following the manufacturer’s instructions or local guidelines is crucial and may involve additional costs.
Software Costs

Some brands of DLP 3D printers require proprietary software to operate. While some printers come with their slicing software, often these are basic versions and may lack certain features. Purchasing the full version or switching to premium third-party slicing software can raise costs.
Applications and Industries Using DLP 3D Printing
DLP 3D printing technology has been adopted in various sectors due to its high precision and detailed results. Here are some key applications:
Dentistry
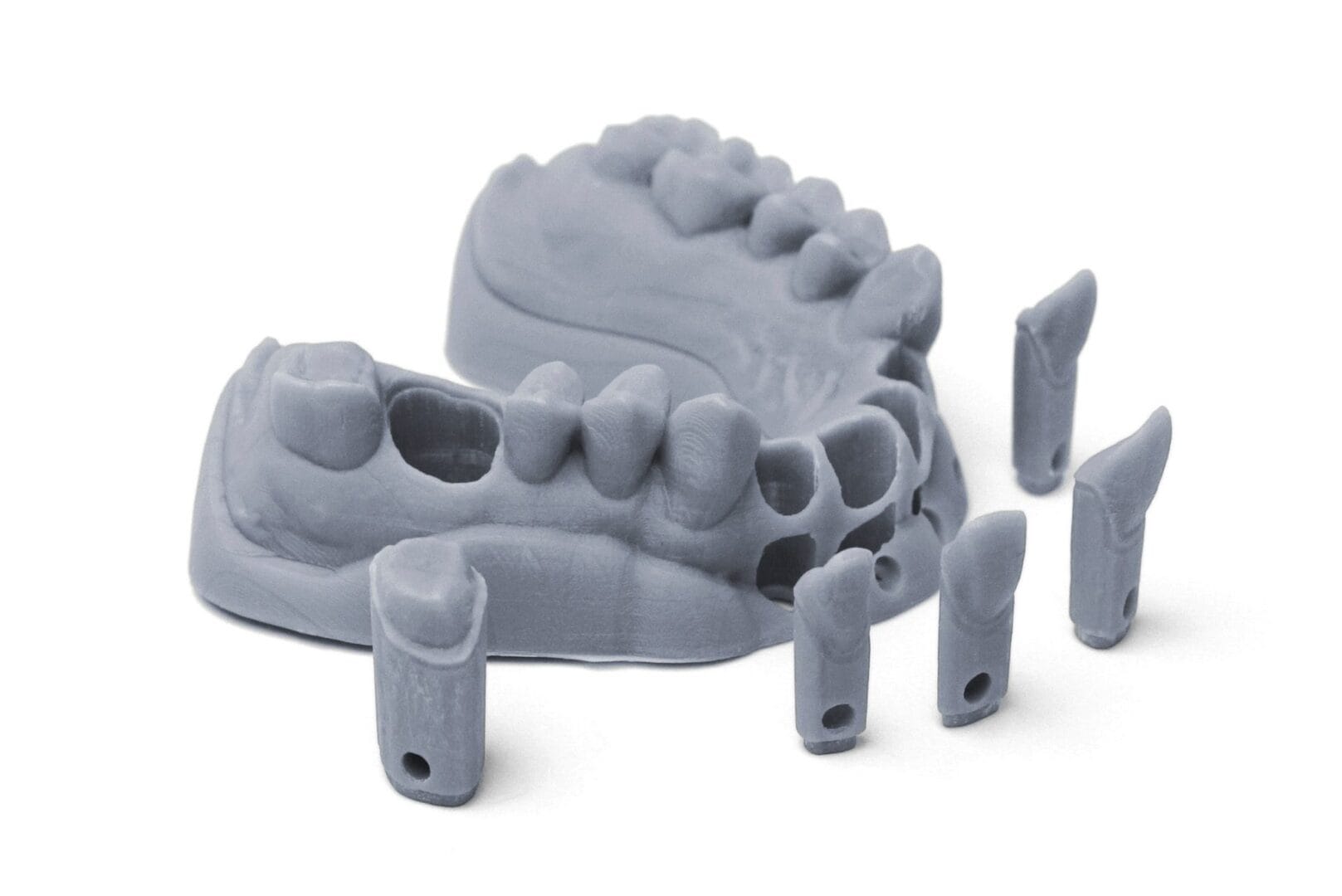
In dentistry, DLP 3D printers are beneficial for making dental models, orthodontic applications, and surgical guides with high reliability and rapid output times. For instance, dental labs can print multiple dental arches in one build platform.
Jewelry
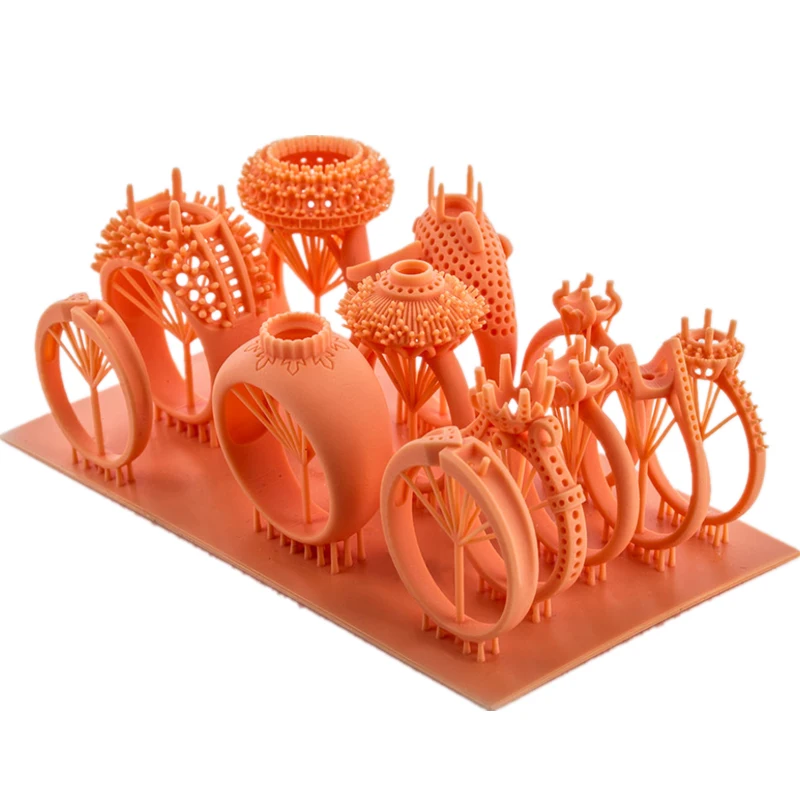
In the world of jewelry, DLP 3D printers serve to provide intricate designs and rapid prototyping capabilities. The high-resolution capabilities of DLP produce models with delicate features and very smooth surface finishes—an essential quality in jewelry design.
Education

In educational institutions, DLP 3D printers are used to make mathematical and scientific models more accessible to students, promoting interactive learning.
Healthcare

From hearing aids to complex organ models for pre-operative planning, DLP 3D printers serve a vital role in the healthcare industry because of their ability to produce highly accurate models swiftly.
In summary, DLP 3D printing plays a significant role in various industries worldwide, proving that it is more than just an innovative technological invention; it is a tool that shapes the future of how we produce and understand things.
The Future Scope of DLP 3D Printing
DLP 3D Printing technology is still in its growing phase and its potential for the future is boundless, reshaping not just how we make things but what we can make.
Fast Prototyping and Manufacturing
The ability to create incredibly detailed parts quickly makes DLP 3D printing ideal for rapid prototyping and quick-turn manufacturing.
Microfabrication
Microfabrication involves the creation of structures with micrometer-scale features. The high-resolution capabilities of DLP 3D printers make them excellent for this, particularly in medical and electronic applications.
Bioprinting
Bioprinting, or the 3D printing of living tissue, is an exciting frontier that can potentially revolutionize medicine. DLP 3D printers can help in this field by creating detailed scaffolds for cells to grow on.
New Materials
Researchers are continually developing new types of resin for DLP 3D printers. These new materials can have very different properties, opening up a wealth of possibilities for the objects that can be printed using DLP technology.
By examining potential growth areas, we can say with certainty that the future of DLP 3D printing is bright and filled with groundbreaking advancements.
Challenges and Limitations of DLP 3D Printing
While DLP 3D printing has proved to be a game-changer in many industries, like every other technology, it too has its challenges and limitations.
Material Limitations
DLP 3D Printing primarily uses photopolymer resin. These resins can be expensive, and the range of materials that can be used with DLP technology is currently limited.
Post Processing
The parts produced by DLP 3D printers usually require post-processing, which can include washing, curing, and support structure removal. This prolongs the overall manufacturing process.
Size Limitations
DLP 3D printers might not be the best choice if you’re looking to print very large parts as they are usually limited to making smaller objects, given the size of the light-projecting DLP chip.
These challenges aren’t insurmountable and in the grand scheme of its benefits, could be regarded more as areas for future development rather than serious hindrances.
Comparison of DLP with Other 3D Printing Technologies
The 3D printing landscape is vast and diverse, with various technologies having their unique advantages and trade-offs. Let’s see how DLP stacks up against some of them:
DLP vs FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
FDM is perhaps the most widely known 3D printing method. It builds parts layer-by-layer from the bottom up by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament. Here’s how DLP and FDM compare:
- Resolution: DLP has a significantly higher resolution than FDM, which can lead to more detail in printed objects.
- Material Options: FDM printers can use a vast array of thermoplastics, from common options like PLA and ABS to more specialty materials like nylon and wood-composites. In contrast, DLP is generally limited to photopolymer resins.
- Printing Speed: DLP typically has a faster build speed because it constructs an entire layer at a time, while FDM has to trace each layer.
DLP vs SLA (Stereolithography)
SLA is another form of 3D printing that also uses photopolymer resin, but it differs significantly in how it forms each layer:
- Resolution: Both DLP and SLA printers can achieve high resolution, but since SLA guides a laser point-by-point across each layer, it can potentially achieve even higher detail than DLP.
- Printing Speed: Like FDM, SLA constructs each layer point-by-point using a laser. Thus, DLP may have faster build speeds for models with a large cross-sectional area.
As with every manufacturing process, the selection of the right 3D printing technology depends largely on what you’re trying to create.
Future of DLP 3D Printing
DLP 3D printing, despite being a relatively new technology, has made a significant impact in various industries. The interest in this technology continues to grow, and with it, the advancements in its capabilities.
Speed and Efficiency Improvements
Developments are being made to increase the speed at which DLP 3D printing can operate. Innovations aimed at allowing simultaneous curing of multiple layers or faster layer curing times are on the horizon.
Material Diversity
The range of resins that can be used with DLP 3D printing is ever-expanding. Continued research into new materials will further enhance the versatility and application of DLP 3D printing.
Larger Build Volumes
While DLP 3D printers have generally been constrained to smaller build volumes, advancements are being made to allow for larger print sizes without sacrificing the precision and detail DLP is known for.
The future for DLP 3D printing looks bright, as innovations not only improve upon the existing strengths of DLP but also diminish its current limitations.



